| Main Portal page | Indices | Projects |
 |
 |

| |
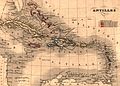
The Caribbean (/ˌkærɪˈbiːən, kəˈrɪbiən/ KARR-ib-EE-ən, kə-RIB-ee-ən, locally /ˈkærɪbiæn/ KARR-ib-ee-an; Spanish: el Caribe; French: les Caraïbes; Dutch: de Caraïben) is a subregion of the Americas that includes the Caribbean Sea and its islands, some of which are surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some of which border both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean; the nearby coastal areas on the mainland are sometimes also included in the region. The region is south-east of the Gulf of Mexico and Northern America, east of Central America, and north of South America.
Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has thousands of islands, islets, reefs, and cays. Island arcs delineate the northern and eastern edges of the Caribbean Sea: the Greater Antilles in the north and the Lesser Antilles, which includes the Leeward Antilles, in the east and south. The nearby Lucayan Archipelago, comprising The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, and the island of Barbados in the Lesser Antilles are considered to be a part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea. All the islands in the Antilles plus the Lucayan Archipelago form the West Indies, which is often interchangeable with the term Caribbean. On the mainland, Belize and the Caribbean coasts of Mexico, Central America, and South America, including the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, Bay Islands Department of Honduras, the North and South Caribbean Autonomous Regions of Nicaragua, the Limón Province of Costa Rica, the Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina, Cartagena, and Barranquilla in Colombia, Maracaibo, Cumaná, and the Federal Dependencies in Venezuela, are also considered culturally Caribbean. French Guiana, Guyana, Panama, and Suriname are often included as parts of the Caribbean due to their political and cultural ties with the region.
Geopolitically, the islands of the Caribbean are often regarded as a subregion of North America, though sometimes they are included in Middle America or left as a subregion of their own; alternately, the term "Caribbean" may have the intended exclusion, or even unintentional inclusion, as part of Latin America. Generally the Caribbean area is organized into 33 political entities, including 13 sovereign states, 12 dependencies, historical disputed territories have existed, and seven other overseas territories. From 15 December 1954 to 10 October 2010, there was a territory known as the Netherlands Antilles composed of five islands, all of which were Dutch dependencies. From 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962, there was also a short-lived political union called the British West Indies Federation composed of ten English-speaking Caribbean territories, all of which were then British dependencies. (Full article...)

Clifford Archibald Roach (13 March 1904 – 16 April 1988) was a West Indian cricketer who played in West Indies' first Test match in 1928. Two years later, he scored the West Indies' first century in Test matches, followed two matches later by the team's first double century. Roach played for Trinidad, but before having any great success at first-class level, he was chosen to tour England with a West Indies team in 1928 and scored over 1,000 runs. When England played in the West Indies in 1930, he recorded his ground-breaking centuries but had intermittent success at Test level afterwards. He toured Australia in 1930–31 and returned to England in 1933, when he once more passed 1,000 runs, but was dropped from the team in 1935. Within three years, he lost his place in the Trinidad team. Roach was generally inconsistent, but batted in an attacking and attractive style. Outside of cricket, he worked as a solicitor. Later in his life, he suffered from diabetes which necessitated the amputation of both his legs. (Full article...)
Selected geography article -

Saint Kitts and Nevis (/-ˈkɪts ... ˈniːvɪs/ ), officially the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain of the Lesser Antilles. With 261 square kilometres (101 sq mi) of territory, and roughly 48,000 inhabitants, it is the smallest sovereign state in the Western Hemisphere, in both area and population, as well as the world's smallest sovereign federation. The country is a Commonwealth realm, with Charles III as King and head of state.
The capital city is Basseterre, located on the larger island of Saint Kitts. Basseterre is also the main port for passenger entry (via cruise ships) and cargo. The smaller island of Nevis lies approximately 3 km (2 mi) to the southeast of Saint Kitts, across a shallow channel called The Narrows. (Full article...)
Selected fare or cuisine -

Moronga, rellena, morcilla or mbusia is a kind of blood sausage. It is found in Argentina, Cuba, Colombia, Puerto Rico, Central America, Mexican and Paraguay cuisine. Spices, herbs (such as ruta, oregano, and mint), onions and chili peppers are added and then boiled in the pig's large intestines for casing for several hours. It is served in a sauce, either "chile rojo" or "chile verde". It is also served in central Mexico as a filling in gorditas and tacos after it has been pan-fried with fresh onions and jalapeño peppers. This sausage is called "morcilla" in the Yucatán Peninsula, and it is almost always served along with other sausages (buche) and a mix of pickled onion, cilantro, and spices. (Full article...)
Did you know? -

- ...that Sammy Sosa from the Dominican Republic has hit more than 60 home runs in a U.S. Major League Baseball season three times, the only player in history to do so?
- ...that in 1766, Santiago de Cuba was almost completely destroyed by an earthquake?
- ...that Eugenia Charles, the Prime Minister of Dominica from July 21, 1980 until June 14, 1995, was the first female prime minister in the Caribbean?
Related portals
Wikiproject
The Lesser Antillean macaw or Guadeloupe macaw (Ara guadeloupensis) is a hypothetical extinct species of macaw that is thought to have been endemic to the Lesser Antillean island region of Guadeloupe. In spite of the absence of conserved specimens, many details about the Lesser Antillean macaw are known from several contemporary accounts, and the bird is the subject of some illustrations. Austin Hobart Clark described the species on the basis of these accounts in 1905. Due to the lack of physical remains, and the possibility that sightings were of macaws from the South American mainland, doubts have been raised about the existence of this species. A phalanx bone from the island of Marie-Galante confirmed the existence of a similar-sized macaw inhabiting the region prior to the arrival of humans and was correlated with the Lesser Antillean macaw in 2015. Later that year, historical sources distinguishing between the red macaws of Guadeloupe and the scarlet macaw (A. macao) of the mainland were identified, further supporting its validity.
According to contemporary descriptions, the body of the Lesser Antillean macaw was red and the wings were red, blue and yellow. The tail feathers were between 38 and 51 cm (15 and 20 in) long. Apart from the smaller size and the all-red coloration of the tail feathers, it resembled the scarlet macaw and may, therefore, have been a close relative of that species. The bird ate fruit – including the poisonous manchineel, was monogamous, nested in trees and laid two eggs once or twice a year. Early writers described it as being abundant in Guadeloupe, but it was becoming rare by 1760, and only survived in uninhabited areas. Disease and hunting by humans are thought to have eradicated it shortly afterward. The Lesser Antillean macaw is one of 13 extinct macaw species that have been proposed to have lived in the Caribbean islands. Many of these species are now considered dubious because only three are known from physical remains, and there are no extant endemic macaws on the islands today. (Full article...)
Selected image -

View of the sea from Tortola, the largest and most populated of the British Virgin Islands.
Selected music -
Hip hop music arrived in Cuba via radio and TV broadcasts from Miami. During the 1980s hip hop culture in Cuba was mainly centered on breakdancing. But by the 1990s, with the collapse of the Soviet Union and the onset of the Special Period, young raperos, exposed to foreign tourists whose wealth highlighted their struggle, turned to rapping to affirm their cubanidad and advocate for further revolutionary reforms. (Full article...)
General images
Caribbean topics
Categories
New articles
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2024-10-06 19:41 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- Walford Gumbs (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cheney123 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-10-06, score: 16
- Wedson (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Roastedbeanz1 (talk · contribs · new pages (144)) started on 2024-10-06, score: 16
- The Real Housewives Ultimate Girls Trip: RHONY Legacy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Isiflgawiki (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-10-06, score: 16
- Oricon Combined Albums Chart (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by IanTEB (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-06, score: 16
- Deaths in September 2024 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rusted AutoParts (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-06, score: 24
- Amanece en Samaná (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Asqueladd (talk · contribs · new pages (41)) started on 2024-10-06, score: 16
- Princess Margaret Hospital, Nassau (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ashlar (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-10-06, score: 32
- Back of Beyond (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shhhnotsoloud (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-10-06, score: 16
- Facebook Gaming (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tajotep (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 16
- Puerto Rico Bank (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tektonson (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 123
- HMS Swallow (1744) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pickersgill-Cunliffe (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 24
- 2024 CONCACAF Caribbean Cup knockout stage (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tomrtn (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 44
- Guanahacabibes camp (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mangokeylime (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 16
- Hurricane Milton (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Vida0007 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 16
- Voltes V: Legacy – The Cinematic Experience (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SafariScribe (talk · contribs · new pages (222)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 16
- Mister Global 2024 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Nkospeep2 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 16
- Lockhart Gardens Shopping Center (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Avengers350 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 32
- Meanings of minor-planet names: 33001–34000 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Absolutiva (talk · contribs · new pages (48)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 16
- Arbizu (surname) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Toweli (talk · contribs · new pages (72)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 16
- Conrado Walter Massaguer (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Guylaen (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 16
- Pierre Bauduy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lisztmacher (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 64
- Damion Davy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GeorgeMHall (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 24
- Shreyas Smith (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GeorgeMHall (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-10-05, score: 24
- 2024–25 Fordham Rams men's basketball team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bremerton98310 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 28
- Narciso Boué (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pietaster (talk · contribs · new pages (35)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 43
- Marcelina Rodríguez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pietaster (talk · contribs · new pages (35)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 51
- Bava (musician) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KEA2024 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 16
- Jocelyne Guilbault (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SoundingCharacters (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 56
- Battle of Muddy Flat (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Historyguy1138 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 16
- Carol leeming (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TrevorGlynLocke (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 16
- Kidnapping Inc. (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bearcat (talk · contribs · new pages (184)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 16
- Cabomba haynesii (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Conan Wolff (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 16
- Anacaona 27 Tower (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JeyReydar97 (talk · contribs · new pages (47)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 32
- Miss Tourism World (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mims Mentor (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 24
- Minister without portfolio (Netherlands) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ætoms (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 16
- Enrique de la Osa (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Guylaen (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 16
- List of ambassadors of Sweden to Colombia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Saftgurka (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 24
- 2022 Caribbean diving disaster (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by The Anome (talk · contribs · new pages (17)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 32
- 2024 Pont-Sondé attack (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Abcmaxx (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 16
- Jomo Pitterson (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GeorgeMHall (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 16
- Syncesia farinacea (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Esculenta (talk · contribs · new pages (60)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 43
- Dewey University (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Immewnity (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-10-04, score: 24
- Quinton Lightbourne (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Matrixblue (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-03, score: 16
- Henry Jardine Hallowes (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Solo4701 (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2024-10-03, score: 32
- Battle of Santiago (1863) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-10-03, score: 24
- Maria Muntañola Cvetković (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Miraclepine (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-10-03, score: 16
- Succession season 4 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mjks28 (talk · contribs · new pages (241)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 16
- Max60 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rohitkumar096 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-03, score: 56
- Grizel (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Clarityfiend (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2024-10-03, score: 16
- Spoors & Sprenger (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Johan Francke (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-03, score: 24
- Carlacia Grant (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (92)) started on 2024-10-03, score: 32
- Burton–Nibbs International Airport (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 56
- Jennifer L. Morgan (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ForsythiaJo (talk · contribs · new pages (25)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 16
- South Asians in the Netherlands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bkissin (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 16
- Colombian Communist Youth (JUCO) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mason7512 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 16
- Sean Combs sexual misconduct allegations (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Badbluebus (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-09-30, score: 16
- DJ Luian (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 222 Georgi (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Fredrik Lidströmer (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GustenGast (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 16
- 2011 NACRA Rugby Championship (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dave mars (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 80
- Spain at the World Artistic Gymnastics Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mypurplelightsaber (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 16
- Matthew v The State (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tom Morris (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 32
- Bacá (mythological creature) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 35
- 2024 famine in Haiti (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Noble Attempt (talk · contribs · new pages (19)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 24
- José Meléndez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Captain Parmenter (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-10-02, score: 16
- José Meléndez (pitcher, born 1908) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Captain Parmenter (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-10-01, score: 16
- Aaron Pierre (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ortizesp (talk · contribs · new pages (54)) started on 2024-10-01, score: 16
- 18 Dominican Brumaire (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-10-01, score: 44
- Canciones del Alma (album) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Brumendez (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-10-01, score: 16
- Grito del Capotillo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-10-01, score: 48
- Camponotus inaequalis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 2003 LN6 (talk · contribs · new pages (19)) started on 2024-10-01, score: 32
- Amaea retifera (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JoJan (talk · contribs · new pages (36)) started on 2024-10-01, score: 16
- Edwin Rosario vs. Julio César Chávez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beast from da East (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-10-01, score: 16
- Yolaine (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Roastedbeanz1 (talk · contribs · new pages (144)) started on 2024-10-01, score: 16
- Arthur Werner Lewey (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Atchom (talk · contribs · new pages (59)) started on 2024-09-30, score: 16
- Diane T. Capehart (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MoviesandTelevisionFan (talk · contribs · new pages (52)) started on 2024-09-30, score: 16
- The Weight of Chains 3 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by UrbanVillager (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-09-30, score: 16
- Asians in the Netherlands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ThatBritishAsianDude (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 96
- Corey Lane (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (47)) started on 2024-09-30, score: 16
- Sandra Husbands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (47)) started on 2024-09-30, score: 16
- List of slavery-related memorials and museums (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DotCoder (talk · contribs · new pages (50)) started on 2024-09-30, score: 16
- TON S180 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Galaxybeing (talk · contribs · new pages (23)) started on 2024-09-30, score: 16
- Crosspoint (film) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bienvenido Benny Kobayashi (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-09-30, score: 16
- Legislative history of United States four-star officers, 1899–1946 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Morinao (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-09-30, score: 16
- Violence against LGBTQ people (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MikutoH (talk · contribs · new pages (28)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 40
- Mahfood (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tutwakhamoe (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 16
- Célita Soulouque (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Willthacheerleader18 (talk · contribs · new pages (27)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 32
- Santa Maria in Gradi, Viterbo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rococo1700 (talk · contribs · new pages (43)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 16
- Sikhism in Trinidad and Tobago (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jattlife121 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 24
- Shaqkere Parris (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (92)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 48
- Nathan Edward (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (92)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 32
- LGBTQ rights in Paraguay (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RodRabelo7 (talk · contribs · new pages (57)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 16
- Dwayne M. DeGraff (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MoviesandTelevisionFan (talk · contribs · new pages (52)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 16
- Joshua Christie (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GeorgeMHall (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 16
- Roberto García Pantoja (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GeorgeMHall (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 16
- Porta Romana, Viterbo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rococo1700 (talk · contribs · new pages (43)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 16
- Charles Brewster Wheeler (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Billmckern (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-09-29, score: 16
- Jane L. Parpart (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SusunW (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-28, score: 24
- Gold Fang (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Roastedbeanz1 (talk · contribs · new pages (144)) started on 2024-09-28, score: 16
- Vampiros (song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Serggg.02 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-09-28, score: 16
- Portuguese Curaçaoans (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by FARFALLA66 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 32
- Jean François Canonge (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tzim78 (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 24
- Hurricane Helene (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Felicia777 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 48
- Athletics at the 1986 Central American and Caribbean Games – Results (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pietaster (talk · contribs · new pages (35)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 59
- Economy of Penang (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HundenvonPenang (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Álvaro Díaz (rapper) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mooonswimmer (talk · contribs · new pages (20)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 16
- Soltera (Lunay, Chris Jeday and Gaby Music song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tbhotch (talk · contribs · new pages (32)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 24
- 2024 Festival du nouveau cinéma (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bearcat (talk · contribs · new pages (184)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 16
- 2024 in Florida (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thief-River-Faller (talk · contribs · new pages (83)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 24
- List of Cayman Islands women Twenty20 International cricketers (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mitratanmoy (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 16
- Eating the cats (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Miminity (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 16
- Altidor (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Edwardx (talk · contribs · new pages (59)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 16
- Pseudopeltula (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Esculenta (talk · contribs · new pages (60)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 16
- 1977 Aruba general strike (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by FARFALLA66 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-27, score: 48
- HMS Regulus (1785) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pickersgill-Cunliffe (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 40
- Raquel Dexter (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by David Eppstein (talk · contribs · new pages (17)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 32
- Faustin Charles (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Proscribe (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 40
- St Anne's Church, Liverpool (1772–1871) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BarrelProof (talk · contribs · new pages (45)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Aire: Just Breathe (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Phantom Oficiall (talk · contribs · new pages (47)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Suze Youance (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wellington Bay (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Enemy Activities Investigation Service (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Guylaen (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Haitian Bridge Alliance (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Nowa (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Laborie (disambiguation) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PARAKANYAA (talk · contribs · new pages (60)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Cuban Bureau of Investigation (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Guylaen (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Mariano Faget (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Guylaen (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Mariano Faget Jr. (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Guylaen (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Jose Imperatori (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Guylaen (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Riveron (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PigeonChickenFish (talk · contribs · new pages (55)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Pan Am (1998–2004) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ceelidstar (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 40
- Claudine Griggs (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thisbe Schultz (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- P.M. affair (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mangokeylime (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- List of escarpments (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Volcanoguy (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-09-26, score: 16
- Enrique Gay García (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by James E. Scholz (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 16
- Alan Vera (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Nayyn (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-09-25, score: 16
- Cartoon Network (French TV channel) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Benmathieson901 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-25, score: 16
- Integrated Power Services (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Vlu1cker25tj (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-09-25, score: 16
- Puerto Rico-Virgin Islands Microplate (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tektonson (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-25, score: 59
- Venezuelan English Creole (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by FARFALLA66 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-25, score: 80
- List of areas depopulated due to climate change (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Noble Attempt (talk · contribs · new pages (19)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 16
- Jacinta A. Opara (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ugwulebo (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 16
- Enrique Riveron (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by James E. Scholz (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 16
- Jamaica Association for the Deaf (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by More02109 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 32
- Hurricane Helene (2024) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MarioProtIV (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 48
- Academic freedom in Catholic universities (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dmanier (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 16
- Moncho Loubriel (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Eljohnson15 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 16
- Grassroots dictatorship (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mangokeylime (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 16
- Lists of reptiles of France (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Chaotic Enby (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 48
- Mariano Faget Diaz (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Guylaen (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 16
- Expedition to the Unare (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HistoriadorAD (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 16
- N204 highway (Philippines) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Whoislibs (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 16
- Amaga expatria (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jeanloujustine (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-24, score: 40
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Trade and Barbuda Affairs (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 40
- Headshot (Anuel AA song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 222 Georgi (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 16
- Government ministries of Antigua and Barbuda (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 32
- Tropical Storm Helene (2024) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MarioProtIV (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 48
- Daniel López Romo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Eljohnson15 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 16
- 2024 social unrest in Martinique (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Noble Attempt (talk · contribs · new pages (19)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 56
- Bachata: A Social History of a Dominican Popular Music (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WhisperToMe (talk · contribs · new pages (372)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 32
- Binu Bairam (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Narcis90 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 16
- Fédération Internationale d'Escrime (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bkonrad (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 88
- Manuel Benitez Valdés (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Guylaen (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 24
- José Ramirez Pantoja (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bww3 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 16
- Cartoon Network (Europe) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 2601:152:5082:19F0:E18C:F066:D876:1D09 (talk · contribs · new pages (0)) started on 2024-09-23, score: 16
- Nilda (given name) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rosiestep (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-09-22, score: 16
- Luis Kalaff (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WhisperToMe (talk · contribs · new pages (372)) started on 2024-09-21, score: 16
- Liset (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Duckmather (talk · contribs · new pages (42)) started on 2024-09-22, score: 16
- Herbert MacDonald (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tassedethe (talk · contribs · new pages (205)) started on 2024-09-22, score: 16
- Roland Scott (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tassedethe (talk · contribs · new pages (205)) started on 2024-09-22, score: 16
- November 1978 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mandsford (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-09-22, score: 40
- Real Hasta la Muerte 2 Tour (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 222 Georgi (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-22, score: 16
- Order of battle at the Battle of Yungay (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DonBeroni (talk · contribs · new pages (119)) started on 2024-09-22, score: 16
- Gloria Rodriguez Calero (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ipigott (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-09-22, score: 16
- Heinz Lüning (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Guylaen (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-09-22, score: 40
- Arubans in the United States (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by FARFALLA66 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-22, score: 48
- History of Antigua and Barbuda (1962-1967) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-09-15, score: 56
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Shortcuts to this page: Portal:West Indies • P:CARIB Purge server cache